When you apply for a credit card, personal loan, or any other type of credit, the lender must first evaluate if you are a good credit risk. When assessing credit risk, a lender looks at the ability of a borrower to meet loan obligations which will to some extent determine the pricing of the loan.
The success of your loan application largely depends on the following:
The 3Ps of Credit:
1) Purpose of borrowing
Lenders want to know why you are borrowing to assess the risk involved. The type of loan is then matched to your purpose for borrowing. If you are buying a house, then it is a housing loan while a hire purchase loan would be given to finance a car. The purpose and whether the loan is secured or unsecured, will among others, determine the interest rate and tenure of the loan.
2) Payment ability
Your repayment capacity is vital. Lenders are keen to see enough surplus income or cash reserve to meet your new financial commitments. They would like to be assured of your stable income or continuity of employment. Here, your cash flow position is being evaluated. An important indicator of your payment ability is your debt-to-income ratio.
3) Payment history
Your past track records on repayments of your earlier or existing loans are looked at to determine what type of paymaster you are, especially if your chances of getting a new loan are slim.
Debt-To-Income Ratio
A debt-to-income ratio indicates a person’s total monthly loan repayments against his gross monthly income. A high ratio indicates that a person may not have enough cash for his monthly needs.
As a general rule, your total monthly repayment on all your loans and credit card debt should not be more than 40% of your gross monthly income.
Let us illustrate this point by working out an example of debt-to-income ratio for Encik Daud:
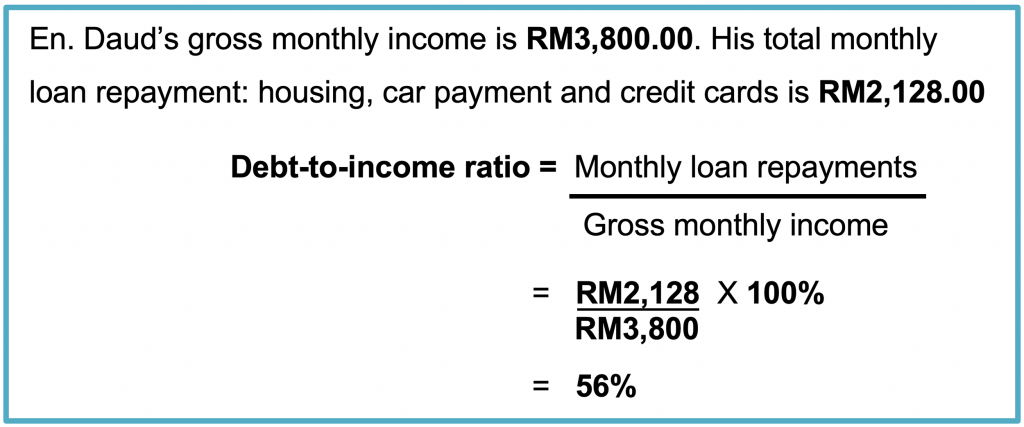
En. Daud’s debt-to-income ratio is higher than the recommended amount. In this scenario, it is best that he strives to bring down the ratio.
So how do you bring down your debt-to-income ratio?
You can either increase your income and/or lower your loan commitments.
It is important not to over commit on loans and purchases using credit cards as this would have an impact on your ratio and in turn may affect your creditworthiness.



